Zhongjing Cheng1, Chengyu Weng1*, Stephan Steinke2,3 and Mahyar Mohtadi2
1 State Key Laboratory of Marine Geology, Tongji University, Shanghai, China.
2 MARUM–Center for Marine Environmental Sciences, University of Bremen, Bremen, Germany.
3 Department of Geological Oceanography and State Key Laboratory of Marine Environmental Science, Xiamen University, Xiamen, China.
*e-mail: weng@tongji.edu.cn
Abstract:
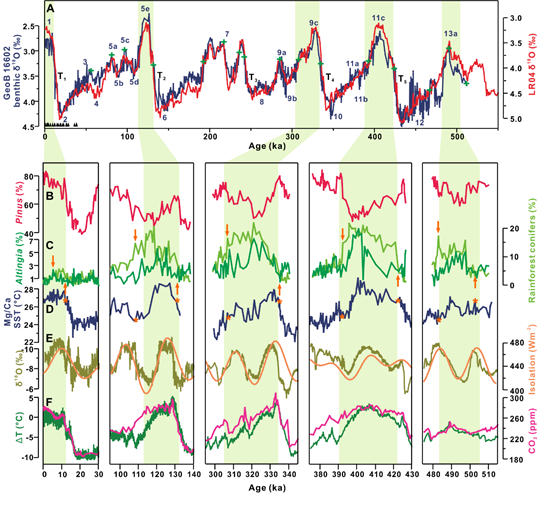
Vegetation dynamics during previous warm interglacial periods shed light on the human impacts on natural ecosystems during the Holocene. However, reliable terrestrial records that span such periods are rare and provide little information on regional scale. Here we present a high-resolution marine pollen record from the northern South China Sea, which reveals that during five peak interglacial periods, Marine Isotope Stages 13a, 11c, 9c, 5e and 1 (the Holocene), the vegetation successions in southern China were similar. At the beginning of each interglacial period, tropical rainforest conifers, which include Dacrydium, Dacrycarpus and Podocarpus, and associated broadleaved taxa, such as Altingia, expanded quickly at the expense of the subtropical/temperate montane conifer Pinus. Near the end of the warm periods, Pinus recovered and the tropical taxa retreated. However, the Holocene displays subtle but significant differences in which the species turnover was interrupted and the rainforest conifers did not fully expand. The Mg/Ca-based sea surface temperature record from the same site reveals that temperature was the major control of the rise and fall of the peak interglacial vegetation. However, exceptionally high charcoal fluxes during the Holocene suggest that human activities through land-use modifications completely, and possibly permanently, altered the natural vegetation trend five to six thousand years ago.
Full article: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41561-018-0250-1


