Xingxing Wang a, Zhimin Jian a, *, Andreas Lückge b, Yue Wang a, Haowen Dang a, Mahyar Mohtadi c
a. State Key Laboratory of Marine Geology, Tongji University, 200092 Shanghai, China
b. Federal Institute for Geosciences and Natural Resources, 30655 Hannover, Germany
c. MARUM-Center for Marine Environmental Sciences, University of Bremen, 28359 Bremen, Germany.
Abstract:
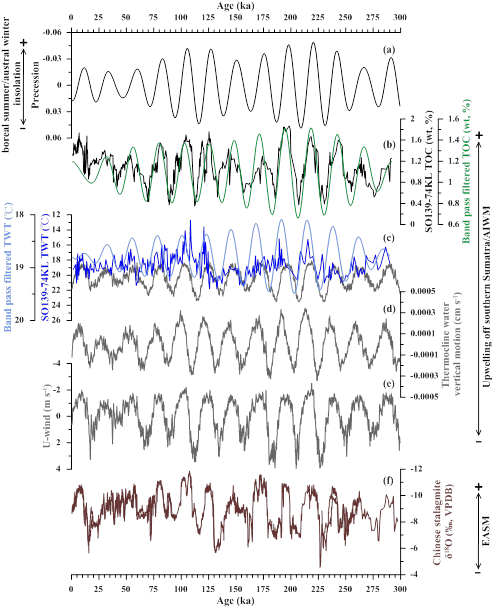
Modern variations of sea surface temperature (SST) and thermocline water temperature (TWT) off southern Sumatra are responding to local upwelling conditions which are controlled by the Australian-Indonesian winter monsoon. The relationships between SST, TWT and upwelling during the past glacial-interglacial cycles are less clearly understood. In this study, SST and TWT variabilities over the past 300 kyr are reconstructed by using foraminiferal Mg/Ca-paleothermometry in sediment core SO139-74KL off southern Sumatra (6°32.6’S, 103°50’E; 1690 m water depth). Whereas SST shows a clear glacial-interglacial cycle, TWT displays a predominant cycle at the precession band. Generally, the TWT record varies with total organic carbon content, revealing that similar to today, TWT and upwelling intensity off southern Sumatra vary in concert during the past 300 kyr. The lack of glacial-interglacial variability in the TWT suggests a limited role of glacial boundary conditions, such as changing sea level and ice volume, on the upwelling intensity in this region. The vertical gradients of upper water δ18O and temperature at this site also reveal precessional cyclicity. Our model simulation of air-sea interaction further supports the low TWTs during periods of enhanced upwelling and precession minimum.
Full article:https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0277379118300246


