Taoliang Zhanga, Rujian Wanga*, Leonid Polyakb, Wenshen Xiaoa
a State Key Laboratory of Marine Geology, TongjiUniversity, Shanghai 200092, China
b Byrd Polar and ClimateResearchCenter, The OhioStateUniversity, Columbus, OH43210, USA
Abstract:
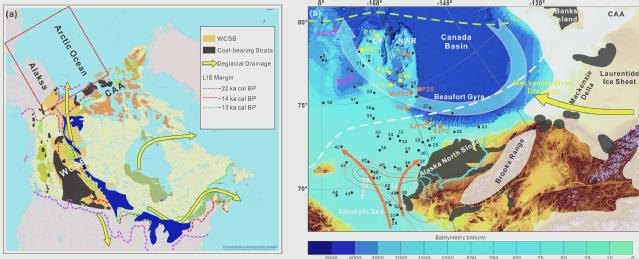
Distribution and composition of coarse particles (>250 µm) were investigated in 13 sediment cores from the Chukchi margin, western Arctic Ocean. Petrographic clast identification is supplemented by XRF core scanning, EDS analysis of coal fragments, and AMS 14C dating of planktic foraminifera for age control. Coal debris distribution is also investigated in surface sediments of the study region for provenance interpretation. The sediment-core study focuses on the interval between the Last Glacial Maximum and the Holocene for constraining provenance and timing of the deglacial discharge. We find that this interval is characterized by a distinct enrichment in sedimentary rock fragments, including coal. Comparison with longer stratigraphic records indicates that this composition is unique for the time interval since at least Maine Isotope Stage 5. Based on the timing, interpreted provenance, and geographic distribution of the coal enrichment, we conclude that the most likely primary source was the deglacial discharge from the Mackenzie drainage basin of the Laurentide Ice Sheet (LIS). The identified coal-bearing layer, also expressed in the XRF sulfur record, can be thus used as a stratigraphic marker for the LIS discharge to the Arctic Ocean during the last deglaciation.
Full Article:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quascirev.2019.06.029