Zhimin Jiana, Yue Wanga, Haowen Danga, David W. Leab, Zhengyu Liuc, Haiyan Jina, and Yaqian Yina
a State Key Laboratory of Marine Geology, Tongji University, 200092 Shanghai, China;
b Department of Earth Science, University of California, Santa Barbara, CA 93106;
c Department of Geography, Ohio State University, Columbus, OH 43210
Abstract:
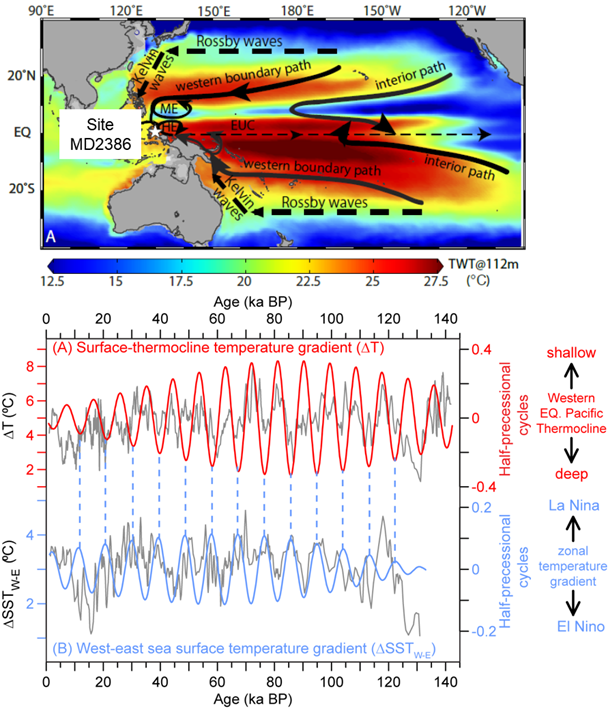
The El Niño−Southern Oscillation (ENSO), which is tightly coupled to the equatorial thermocline in the Pacific, is the dominant source of interannual climate variability, but its long-term evolution in response to climate change remains highly uncertain. This study uses Mg/Ca in planktonic foraminiferal shells to reconstruct sea surface and thermoclinewater temperatures (SST and TWT) for the past 142ky in a western equatorial Pacific (WEP) core MD01-2386. Unlike the dominant 100-ky glacial−interglacial cycle recorded by SST and δ18O, which echoes the pattern seen in other WEP sites, the upper ocean thermal gradient shows a clear half-precessional (9.4 ky or 12.7 ky) cycle as indicated by the reconstructed and simulated temperature(ΔT) and δ18O differences between the surface and thermocline waters. This phenomenon is attributed to the interplay of subtropical-totropical thermocline anomalies forced by the antiphased meridional insolation gradients in the two hemispheres at the precessional band. In particular, the TWT shows greater variability than SST, and dominates the ΔT changes which couple with the west−east SST difference in the equatorial Pacific at the half-precessional band, implying a decisive role of the tropical thermocline in orbital-scale climate change.
Full Article:https://www.pnas.org/content/early/2020/03/11/1915510117